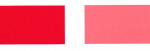
Pigment Czerwony 170
| Nazwa produktu | PIGMENT RED 170 |
| Synonimy | C.I.Pigment Red 170; C.I.PR170; PR170; P.R.170 |
| CI | 12475 |
| Nr CAS | 2786-76-7 |
| EINECS | 220-509-3 |
| Waga molekularna | 454.48 |
| Formuła molekularna | C26H22N4O4 |
| Kolor | Czerwony proszek |
![]()
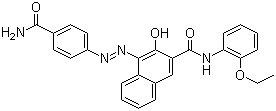
Wzór struktury molekularnej:
Fastness Properties of Pigment Red 170:
| Odporność na światło | 5 |
| Odporność na ciepło (℃) | 180 |
| Wodoodporność | 5 |
| Odporność na olej | 4 |
| Odporność na kwas | 5 |
| Odporność na alkalia | 5 |
| Odporność na alkohol | 4-5 |
Główne zastosowanie: Atrament na bazie wody, Atrament offsetowy, Atrament na bazie rozpuszczalnika, Plastik, Farba, Druk tekstylny
We have various pigment grades and properties to meet different customers’ needs, please specify your application and requirements so that we can recommend accordingly. E-mail: sy@sypigment.com
Product Description of Pigment Red 170:
Pigment Red 170 has stronger than Pigment Red 210, it is a neutral red color and has two crystal forms; the transparent type is blue-red and has a light fastness of level 6, and the non-transparent type has a light fastness of level 7, high hiding power and more stable to solvents; Novoperm Red F2RK The specific surface area of 70 is 23m2/g; it is mainly used in coatings, and can be mixed with molybdenum chrome orange and quinacridone.Mainly used in coatings and solvent printing inks, water-based printing inks, textile printing and dyeing, etc.
Pigment red 170 or PR170 is an organic pigment extensively used in automotive coatings and painting.
It is produced synthetically by converting p-aminobenzamide into the corresponding diazonium compound followed by coupling with 3-hydroxy-2-naphththoic acid (2-ethoxy)anilide ("Naphtol AS-PH" dye precursor).
In the solid state the hydrazo tautomer forms and several crystal structures exist. In the initial α polymorph the molecules are arranged in a herringbone pattern with extensive hydrogen bonding. The φ polymorph is more dense and more stable and produced industrially by thermal treatment in water at 130°C under pressure. In this phase the molecules are planar and arranged in layers. Extensive hydrogen bonding exists within the layer but between layers the only interactions are Van der Waals forces. Dense crystal structures are preferred for pigments used in coatings because in the event of photochemical decomposition the fragments are locked in place and are able to recombine. Research shows that by replacing the ethoxy group in this compound by a methoxy group the crystal structure is less stable and in the final application and the color fades more easily. By careful selection of substituents it is possible to optimize crystal structure and improve optical properties.
TDS (Pigment Red 170) MSDS (Pigment Red 170)Synonimy
- C.I. Pigment Red 170
- 2786-76-7
- PIGMENT RED 170
- UNII-54O6PK8790
- 54O6PK8790
- 4-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)diazenyl]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- 4-[[4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl]azo]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- CI Pigment Red 170
- 2-Naphthalenecarboxamide, 4-((4-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-
- 2-Naphthalenecarboxamide, 4-[[4-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]azo]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-
- 4-4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenylazo-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- Permanent Red F 5RK
- Permanent Red F 3RK70
- C.I. Pigment Red 120
- HSDB 3901
- 4-((4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- EINECS 220-509-3
- EC 220-509-3
- SCHEMBL2139449
- DTXSID7029243
- SCHEMBL12954916
- SCHEMBL14560976
- SCHEMBL16191196
- SCHEMBL21468586
- P.R.266F7RK
- 2-Naphtho-o-phenetidide, 4-((p-carbamoylphenyl)azo)-3-hydroxy-
- ZINC33839056
- ZINC100048551
- 4-((4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthalenecarboxamide
- C.I.12475
- 071N997
- W-109137
- Q15425799
- 2-Naphthalene-carboxamide,3-hydroxy-4-(((4-aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-
- 3-(2-Ethoxyphenylcarbamoyl)-1-[2-(4-carbamoylphenyl)hydrazono]naphthalene-2(1H)-one
- 4-[(E)-(4-carbamoylphenyl)diazenyl]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthamide
- 2-Naphthalenecarboxamide, 4-(2-(4-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl)diazenyl)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-
Nazwa IUPAC: 4-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)diazenyl]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
InChI: InChI=1S/C26H22N4O4/c1-2-34-22-10-6-5-9-21(22)28-26(33)20-15-17-7-3-4-8-19(17)23(24(20)31)30-29-18-13-11-16(12-14-18)25(27)32/h3-15,31H,2H2,1H3,(H2,27,32)(H,28,33)
InChKlucz: BGVYDWVAGZBEMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Kanoniczne UŚMIECH: CCOC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=O)C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C2O)N=NC4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)N
| Nazwa właściwości | Wartość nieruchomości |
| Waga molekularna | 454.5 |
| XLogP3-AA | 5.2 |
| Liczba dawców wiązania wodorowego | 3 |
| Liczba akceptorów wiązania wodorowego | 6 |
| Obrotowa liczba obligacji | 7 |
| Dokładna masa | 454.1641052 |
| Masa monoizotopowa | 454.1641052 |
| Topologiczna powierzchnia polarna | 126 Ų |
| Liczba ciężkich atomów | 34 |
| Formalna opłata | 0 |
| Złożoność | 724 |
| Liczba atomów izotopu | 0 |
| Zdefiniowana liczba stereocentrum atomów | 0 |
| Niezdefiniowana liczba stereocentrum atomów | 0 |
| Zdefiniowana liczba stereocentrów wiązania | 0 |
| Niezdefiniowana liczba stereocentrów wiązania | 0 |
| Liczba jednostek wiązanych kowalencyjnie | 1 |
| Związek jest kanonizowany | TAk |