Pigmentrot 170
| Produktname | PIGMENT ROT 170 |
| Synonyme | CIPigment Rot 170; CIPR170; PR170; PR170 |
| CI | 12475 |
| CAS-NR. | 2786-76-7 |
| EINECS | 220-509-3 |
| Molekulargewicht | 454.48 |
| Molekularformel | C26H22N4O4 |
| Farbe | Rotes Pulver |
![]()
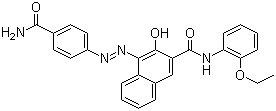
Molekülstrukturformel:
Echtheitseigenschaften von Pigment Red 170:
| Lichtgeschwindigkeit | 5 |
| Hitzebeständigkeit (℃) | 180 |
| Wasserbeständigkeit | 5 |
| Ölbeständigkeit | 4 |
| Säurebeständigkeit | 5 |
| Alkalibeständigkeit | 5 |
| Alkoholbeständigkeit | 4-5 |
Hauptanwendung: Tinte auf Wasserbasis, Offsettinte, Tinte auf Lösungsmittelbasis, Kunststoff, Farbe, Textildruck
Wir haben verschiedene Pigmentqualitäten und -eigenschaften, um den unterschiedlichen Kundenanforderungen gerecht zu werden. Bitte geben Sie Ihre Anwendung und Anforderungen an, damit wir sie entsprechend empfehlen können. E-Mail: sy@sypigment.com
Produktbeschreibung von Pigment Red 170:
Pigment Red 170 ist stärker als Pigment Red 210, es ist eine neutrale rote Farbe und hat zwei Kristallformen; der transparente Typ ist blau-rot und hat eine Lichtechtheit von Stufe 6 und der nicht transparente Typ hat eine Lichtechtheit von Stufe 7, hohe Deckkraft und stabiler gegenüber Lösungsmitteln; Novoperm Red F2RK Die spezifische Oberfläche von 70 beträgt 23m2/g; Es wird hauptsächlich in Beschichtungen verwendet und kann mit Molybdän-Chromorange und Chinacridon gemischt werden. Wird hauptsächlich in Beschichtungen und Lösungsmitteldruckfarben, Druckfarben auf Wasserbasis, Textildruck und -färben usw. verwendet.
Pigment red 170 or PR170 is an organic pigment extensively used in automotive coatings and painting.
It is produced synthetically by converting p-aminobenzamide into the corresponding diazonium compound followed by coupling with 3-hydroxy-2-naphththoic acid (2-ethoxy)anilide ("Naphtol AS-PH" dye precursor).
In the solid state the hydrazo tautomer forms and several crystal structures exist. In the initial α polymorph the molecules are arranged in a herringbone pattern with extensive hydrogen bonding. The φ polymorph is more dense and more stable and produced industrially by thermal treatment in water at 130°C under pressure. In this phase the molecules are planar and arranged in layers. Extensive hydrogen bonding exists within the layer but between layers the only interactions are Van der Waals forces. Dense crystal structures are preferred for pigments used in coatings because in the event of photochemical decomposition the fragments are locked in place and are able to recombine. Research shows that by replacing the ethoxy group in this compound by a methoxy group the crystal structure is less stable and in the final application and the color fades more easily. By careful selection of substituents it is possible to optimize crystal structure and improve optical properties.
TDS (Pigment Red 170) MSDS (Pigment Red 170)Synonyme
- C.I. Pigment Red 170
- 2786-76-7
- PIGMENT RED 170
- UNII-54O6PK8790
- 54O6PK8790
- 4-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)diazenyl]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- 4-[[4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl]azo]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- CI Pigment Red 170
- 2-Naphthalenecarboxamide, 4-((4-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-
- 2-Naphthalenecarboxamide, 4-[[4-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]azo]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-
- 4-4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenylazo-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- Permanent Red F 5RK
- Permanent Red F 3RK70
- C.I. Pigment Red 120
- HSDB 3901
- 4-((4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
- EINECS 220-509-3
- EC 220-509-3
- SCHEMBL2139449
- DTXSID7029243
- SCHEMBL12954916
- SCHEMBL14560976
- SCHEMBL16191196
- SCHEMBL21468586
- P.R.266F7RK
- 2-Naphtho-o-phenetidide, 4-((p-carbamoylphenyl)azo)-3-hydroxy-
- ZINC33839056
- ZINC100048551
- 4-((4-(Aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthalenecarboxamide
- C.I.12475
- 071N997
- W-109137
- Q15425799
- 2-Naphthalene-carboxamide,3-hydroxy-4-(((4-aminocarbonyl)phenyl)azo)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-
- 3-(2-Ethoxyphenylcarbamoyl)-1-[2-(4-carbamoylphenyl)hydrazono]naphthalene-2(1H)-one
- 4-[(E)-(4-carbamoylphenyl)diazenyl]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthamide
- 2-Naphthalenecarboxamide, 4-(2-(4-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl)diazenyl)-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-
IUPAC-Name: 4-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)diazenyl]-N-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxamide
InChI: InChI=1S/C26H22N4O4/c1-2-34-22-10-6-5-9-21(22)28-26(33)20-15-17-7-3-4-8-19(17)23(24(20)31)30-29-18-13-11-16(12-14-18)25(27)32/h3-15,31H,2H2,1H3,(H2,27,32)(H,28,33)
InChIKey: BGVYDWVAGZBEMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Kanonisches Lächeln: CCOC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=O)C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C2O)N=NC4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)N
| Name des Anwesens | Eigentumswert |
| Molekulargewicht | 454.5 |
| XLogP3-AA | 5.2 |
| Anzahl der Wasserstoffbrückenspender | 3 |
| Anzahl der Wasserstoffbindungsakzeptoren | 6 |
| Rotierbarer Bindungszähler | 7 |
| Genaue Masse | 454.1641052 |
| Monoisotopische Masse | 454.1641052 |
| Topologische polare Oberfläche | 126 Ų |
| Schwere Atomzahl | 34 |
| Formale Ladung | 0 |
| Komplexität | 724 |
| Anzahl der Isotopenatome | 0 |
| Definierte Anzahl von Atom-Stereozentren | 0 |
| Undefinierte Anzahl von Atom-Stereozentren | 0 |
| Definierte Bond-Stereocenter-Anzahl | 0 |
| Undefinierter Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Anzahl der kovalent gebundenen Einheiten | 1 |
| Verbindung ist kanonisiert | Ja |